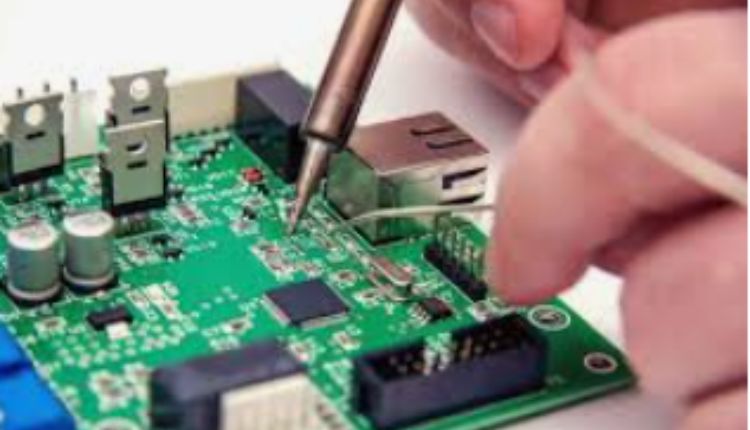
PCB
In the world of electronics manufacturing, SMT and PCBA are two crucial terms that often appear together. Whether you’re a hardware engineer, product developer, or simply curious about how modern electronics are built, understanding what SMT is and how it relates to PCBA can provide valuable insights into the core of electronic production.
This guide will clearly explain what SMT is, what PCBA means, how they work together, and why they are essential in electronics manufacturing.
What is SMT?
SMT, or Surface Mount Technology, is a method for producing electronic circuits in which components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This method differs from traditional through-hole technology, where component leads are inserted into drilled holes on the board.
Key Features of SMT:
- Miniaturization: Components are smaller and lighter.
- Automation-friendly: Highly suitable for automated assembly lines.
- High component density: Allows more components to be placed in a smaller area.
- Cost-efficient: Enables faster production and lower material costs.
Common SMT Components:
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- Transistors
- Diodes
SMT Process Steps:
- Solder Paste Printing: Applying solder paste to PCB pads using a stencil.
- Component Placement: Automated pick-and-place machines position components on the board.
- Reflow Soldering: The board is heated in a reflow oven to melt the solder and secure the components.
What is PCBA?
PCBA, short for Printed Circuit Board Assembly, refers to the complete process of assembling all electronic components onto a PCB. PCBA includes both SMT and through-hole technology (if required), as well as testing and inspection procedures.
In other words, PCBA is the final assembled version of a PCB, ready to be integrated into an electronic device.
PCBA Process Overview:
- Bare PCB Fabrication: Manufacturing the physical board.
- SMT Assembly: Mounting surface-mount components.
- Through-Hole Assembly (if needed): Inserting and soldering traditional components.
- Inspection and Testing: Using AOI, X-ray, ICT, or functional testing.
- Final Cleaning and Packaging
Types of PCBA:
- SMT PCBA (surface-mount only)
- Mixed PCBA (SMT + through-hole)
- Double-sided PCBA (components mounted on both sides)
SMT vs. PCBA: What’s the Difference?
Although closely related, SMT and PCBA are not the same:
Why SMT and PCBA Matter in Electronics
Almost every modern electronic device relies on SMT and PCBA processes to function reliably. From smartphones and laptops to industrial machinery and medical equipment, these technologies ensure the high-quality, high-speed manufacturing of compact, high-performance electronic products.
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Faster assembly cycles.
- Precision: Automated systems minimize human error.
- Scalability: Ideal for large-scale production.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduced labor and material waste.
Choosing a Reliable SMT and PCBA Manufacturer
When selecting a manufacturer for your SMT or PCBA needs, consider the following:
- Experience in handling complex PCB designs
- Certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485, or IATF 16949
- Advanced Equipment, including pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and testing systems
- Strict Quality Control, including 100% inspection and functional testing
A professional SMT and PCBA service provider can ensure smooth product development, quick turnaround, and outstanding reliability.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what SMT is and what PCBA is gives you a clearer picture of how modern electronics are created. SMT is the technological process for mounting components directly onto a PCB, while PCBA represents the complete board assembly ready for use in electronic devices.
If you’re looking for dependable SMT and PCBA services, partnering with an experienced electronics manufacturer ensures high-quality results from prototyping to full-scale production.